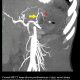
Case 4- Pancreatic pseudocyst with Pseudoaneurysm
March 25, 2020
CASE 6- FAHR’S DISEASE
April 25, 2020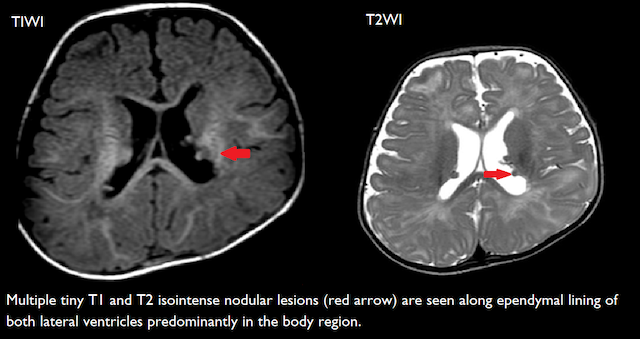
DIAGNOSIS
TUBEROUS SCLEORIS-CNS MANIFESTATIONS
FINDINGS
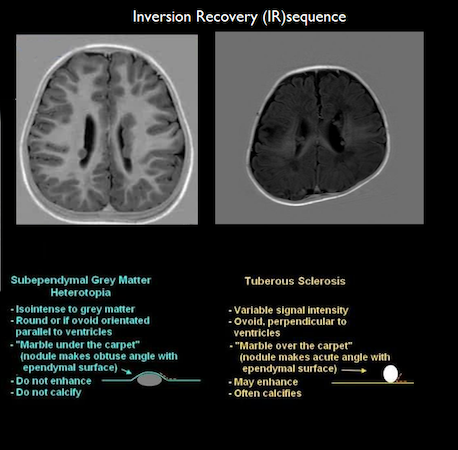
- Multiple tiny T1 and T2 isointense nodular lesions are seen along ependymal lining of both lateral ventricles predominantly in the body region probably representing sub ependymal hemartomas.
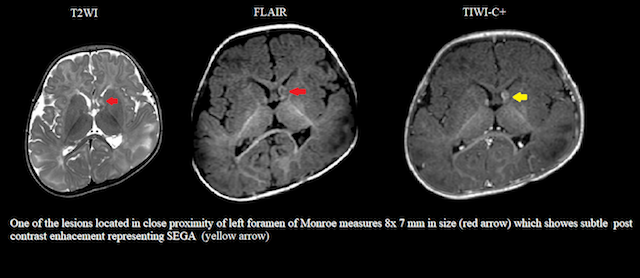
- One of the lesions located in close proximity of left foramen of Monroe shows subtle post contrast enhancement and probably raises the possibility of sub ependymal giant cell astrocytoma.
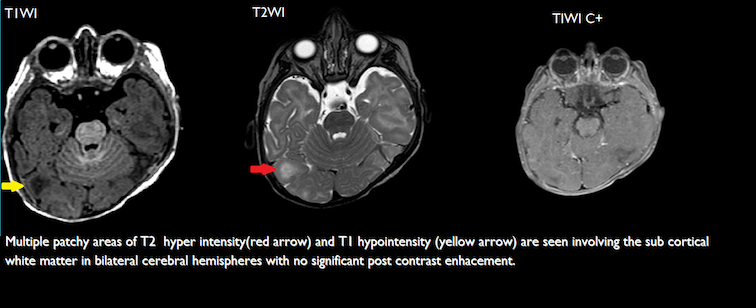
- Multiple patchy areas of T2 and FLAIR hyper intensity and T1 hypointensity are seen involving the sub cortical white matter in bilateral cerebral hemispheres representing cortical subcortical tubers.
DISCUSSION
Tuberous sclerosis is second most common neurocutaneous syndrome characterized by the formation of non-malignant hamartomas, cortical tubers and benign neoplastic lesions with incidence of 1: 5000 live births. It commonly affects skin, brain, retina, lungs, heart, skeleton and kidneys.
The intracranial manifestations include subependymal hamartomas, subependymal giant cell astrocytoma’s (SEGA), cortical tubers and radially oriented linear bands. Commonest lesion is subependymal hamartomas which may be calcified and diagnosed on CT or T2* MRI which also helps to differentiate from other periventricular lesions like heterotropia.SEGA arelarger hamartomas more than 5mm in size, located in the caudothalamic groove near foramen of Monroe whose follow up is needed as they progressively grow at rate of 2.5-5.6 mm/ year and may cause obstructive hydrocephalus.
Subependymal nodules cortical tubers, cardiac rhabdomyoma, renal angiomyolipoma, subependymal giant cell astrocytoma and lymphangioleiomyomatosis are major radiological features. White matter hamartomas, radial migration lines ,hamartomatous rectal polyps ,Non-renal hamartomas ,Bone cysts ,Renal cysts are minor radiological featres
Presence of two of major features or one major and one minor is definite diagnostic of tuberous sclerosis.